Types of Waves: In Physics, waves are a fundamental phenomena that describes the transmission of energy and information through a medium of an empty space. These waves are characterised by their oscillatory motion and are classified into several types based on their nature, propagation mechanism, and the medium they travel through. Let use know about the different types of waves studied in Physics.
Types of Waves
Broadly the waves are of seven types which can further be classified into various types. The main classifications waves are:
- Mechanical waves
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Surface Waves
- Standing Waves
- Seismic Waves
- Gravitational Waves
- Quantum Mechanical Waves
Let us discuss some of them one by one.
Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel through. They propagate energy by causing particles in the medium to oscillate. These can be:
- Transverse Waves: In transverse waves, the oscillations of the medium's particles are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Examples include waves on a string and electromagnetic waves like light.
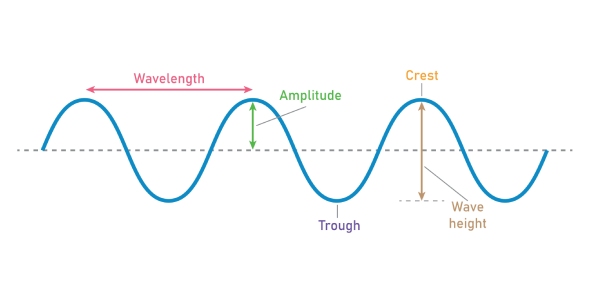
Image Source: Proprofs
- Longitudinal Waves: Longitudinal waves have oscillations parallel to the direction of wave propagation. For example, sound waves in air, where compressions (high-pressure regions) and rarefactions (low-pressure regions) propagate through the medium.
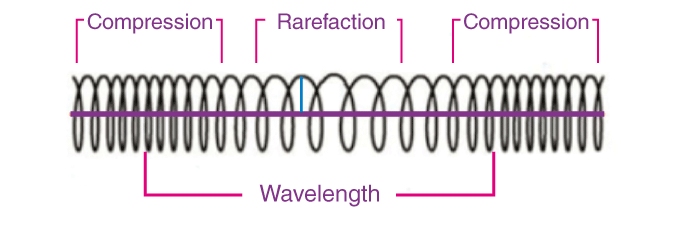
Image Source: Byju’s
Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium and can propagate through a vacuum. They consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave travel. Examples include:
| Radio Waves | Used for communication and broadcasting |
| Microwaves | Used in microwave ovens and communication technologies |
| Infrared | Involved in heat transfer and night vision technology |
| Visible Light | The range of electromagnetic waves visible to the human eye |
| Ultraviolet, X-rays, and Gamma Rays | Higher energy electromagnetic waves used in medical imaging and sterilization |
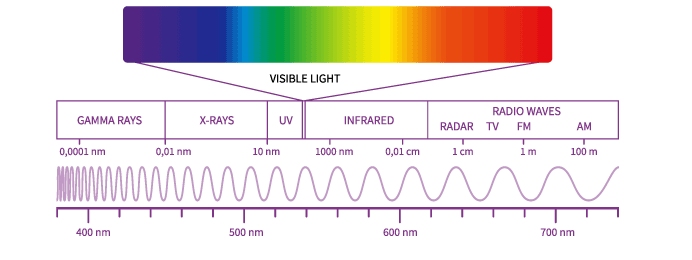
Image Source: Byju’s
Surface Waves
Surface waves travel along the interface between two different media, such as:
| Water Waves | On the surface of oceans, lakes, and ponds |
| Seismic Waves | Waves that travel through the Earth's crust during earthquakes |
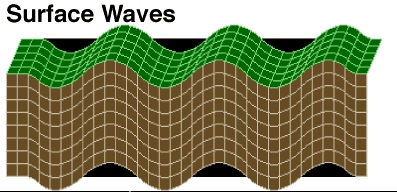
Image Source: USGS.gov
Standing Waves
Standing waves are formed by the interference of two waves traveling in opposite directions within the same medium. They have fixed points of no motion (nodes) and points of maximum oscillation (antinodes). Examples include:
- Vibrations on strings (musical instruments).
- Resonance in pipes and other acoustic systems.
.jpg)
Image Source: Isaac Physics
Seismic Waves
Seismic waves are generated by earthquakes and travel through the Earth's interior. They include:
| P-waves (Primary waves) | Compression waves that travel faster through solids and liquids |
| S-waves (Secondary waves) | Shear waves that propagate slower and only through solids |
.jpg)
Image Source: Byju’s
Gravitational Waves
Gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime caused by accelerating masses, predicted by Einstein's theory of general relativity. They travel at the speed of light and are produced by cataclysmic events like colliding black holes or neutron stars.
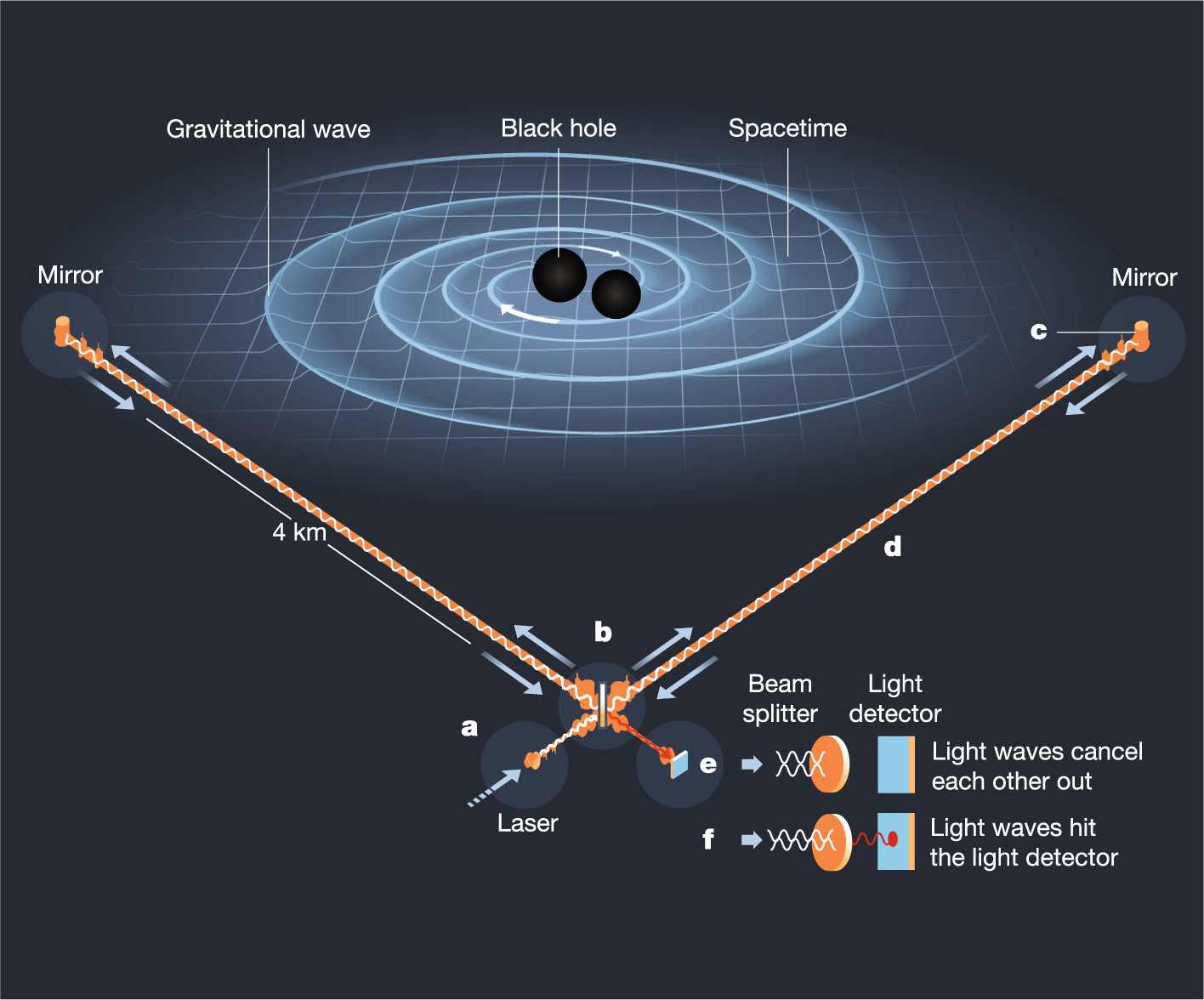
Image Source: Nature
Quantum Mechanical Waves
These waves represent the probability amplitudes of finding particles in different states and play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of particles at the quantum level.
References and Further Reading
- Books
NCERT Class 10 Science Textbook PDF
NCERT Class 12 Physics Textbook PDF
- Articles
Magnetic effects of Electric Current
- Online Resources
CBSE Class 10 Science Video Tutorials
CBSE Class 12 Physics Video Tutorials
Also Check:
